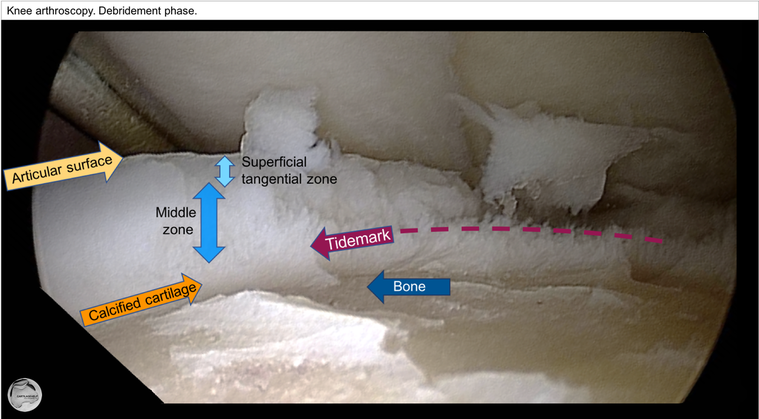
cartilage structure
Cartilage consists of extracellular matrix (ECM) and chondrocytes, which are highly specialised cells. Water (up to 80% of total cartilage mass), collagen, proteoglycans with other proteins compose the ECM. Organisation of chondrocytes together with ECM varies in different cartilage layers to respond the different tasks. Joint cartilage consists of different layers. The most superficial layers has tangential collagen fibers, and a very thin lamina splendens on top of that. Transitional layer has perpendicular collagen fibers, and the deepest layers serve as an attachment layer to bone. This layer communicates with the underlying bone, and it is usually left on place when cartilage delaminates in adults, like seen in following image.
As in any gliding mechanical system, the most superficial layer and lubrication are of utmost importance. Superficial tangential zone in cartilage is critical for proper gliding properties and to integrity of the whole cartilage layer. Vertical rupture of cartilage can be stable in the beginning, but especially in thick cartilage areas loss of tangential integrity forms functionally two individual cartilage areas with no tensile force resistance. This opens up connection into deeper layers and further stresses the tear area, destroying the normal bone protection. Gradually this can lead to increase in size of rupture, and to reactive changes in subchondral bone.
|
|
The content of this website is provided for information only and is not intended to be used for diagnosis or treatment or as a substitute for consultation with your own doctor or a specialist.Email addresses supplied are provided for basic enquiries and should not be used for urgent or emergency requests, treatment of any knee injuries or conditions or to transmit confidential or medical information.
|